Labeled:Z9surbj6cs8= Animal Cells
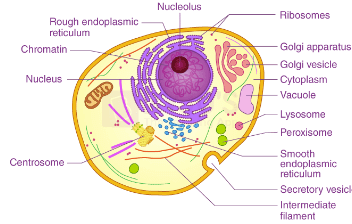
The intricate architecture of animal cells reveals a remarkable interplay of organelles, each fulfilling specialized roles crucial for maintaining cellular integrity and function. From the protective cell membrane to the energy-generating mitochondria, understanding these components is vital for appreciating how cells respond to their environments and contribute to overall organismal health. This complexity raises pertinent questions about the implications of cellular dysfunction and how advanced research can illuminate pathways for therapeutic intervention. As we explore these facets, the relationship between cellular structure and biological processes unfolds in ways that could reshape our understanding of life itself.
Structure of Animal Cells
The structure of animal cells is characterized by a complex arrangement of organelles and membranes that facilitate a variety of biological functions.
The cell membrane delineates the cell’s boundary, while the cytoplasmic matrix supports organelles involved in energy production and cell signaling.
Additionally, the nucleus houses genetic material essential for cell division, ensuring proper cellular function and continuity in multicellular organisms.
See also: Labeled:Uj3t4zt70_Q= United States
Key Organelles and Their Functions
Animal cells contain several key organelles, each playing a specific role in maintaining cellular function and homeostasis.
Mitochondria facilitate energy production, while the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are integral for protein synthesis and modification.
These organelle interactions are crucial for cellular communication, ensuring that signals and materials are efficiently processed and transported, thereby supporting the overall stability and functionality of the cell.
Cellular Processes and Activities
Numerous cellular processes and activities are essential for maintaining the life and functionality of animal cells.
Cellular communication facilitates the exchange of signals, enabling coordinated responses to environmental changes.
Additionally, metabolic pathways are critical for energy production, biosynthesis, and cellular repair.
These interconnected processes ensure cellular homeostasis and adaptability, underpinning the overall health and performance of animal cells in diverse physiological contexts.
Importance of Animal Cells in Biology
Understanding cellular processes and activities provides a foundational perspective on the significance of animal cells within the broader field of biology.
Their cellular diversity underscores evolutionary significance, illustrating how various adaptations facilitate survival in diverse environments.
Furthermore, animal cells are central to understanding disease implications, offering insights into pathological mechanisms, therapeutic targets, and the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments, ultimately enhancing biological knowledge.
Conclusion
In summary, the intricate architecture of animal cells underscores their vital role in sustaining life. Each organelle, a cog in the machinery of cellular function, collaborates to ensure the organism’s survival and adaptability. As the cellular world unfolds, it becomes evident that understanding these microscopic entities is not merely an academic pursuit but a key to unlocking the mysteries of life itself. Ultimately, the study of animal cells serves as a gateway to deeper insights into biological complexity and evolution.